CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Revision Notes Part 1
Chapter 9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production Revision Notes Part 1
Multiple Choice Questions
-
The process of crossing done between different species is known as _______.
-
Control breeding is done with the help of ___________.
-
Which of these is an example of a marine fish? __________
-
____________ is another name for beekeeping.
-
A mule is a cross between _____________.
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Food is necessary for the development and survival of all living things.
- To meet the needs of a growing population, we need to increase food production.
- State-of-the-art technologies such as plant breeding, animal breeding, tissue culture, genetic engineering, and embryo transfer have increased yields many times.
Animal Husbandry
- It is a practice to raise and breed livestock (buffalo, cow, sheep, cow, etc.).
- This includes poultry farming and fishing.
- Dairy farm management and poultry farm management are necessary to select excellent breeds with high yield potential and disease-resistant breeds.

Source: Animal husbandry
Animal Breeding
Breeds are a group of animals of the same species related to their ancestors and share common characteristics and appearance. There are two types of breeding: inbreeding and outbreeding.
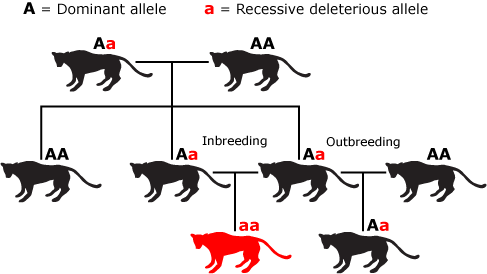
Inbreeding
- It refers to four to six generations of breeding between males and females of the same breed.
- Superior males and females are chosen and matched for this reason.
- Inbreeding encourages homozygosity and is necessary for the evolution of pure lines or genuine breeding species, as in Mendel’s experiment.
- Inbreeding eliminates undesired genes while increasing the number of excellent genes.
- Continuous inbreeding causes inbreeding depression.
- Here, production and fertility decline but may be restored by mating with superior animals who are unrelated.
Outbreeding
It refers to the mating of animals who are not related. There are three varieties of this:
- Out-crossing: is the mating of animals of the same breed who haven’t shared an ancestor in a few generations. This aids in the treatment of depression caused by inbreeding.
- Cross-breeding: It allows two breeds‘ excellent qualities to be combined. Superior males of one breed are mated with superior females of another breed for this reason.
Hisardale is a new breed of sheep that has been established in Punjab as a result of crossbreeding of Marino rams (males) and Bikaneri ewes (females).
- Interspecific hybridization is the cross-breeding of two related but not identical species.
Mule– A mule is a cross between a male donkey and a female horse.
Controlled breeding studies are carried out to address several issues that arise during regular mating.
Control breeding is accomplished using artificial insemination, and semen can be utilized right away or frozen and transferred for later use.
MOET
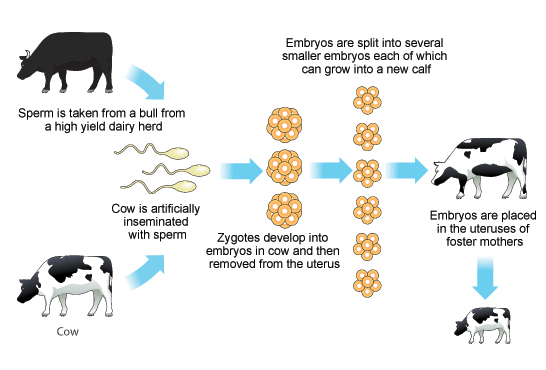
- Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology: Improves the odds of successful hybridization.
- To encourage follicular maturation, the cow is administered hormones equivalent to FSH (Follicle-stimulating hormone).
- Compared to a typical cycle, this leads to more (6-8) eggs.
- The fertilized eggs (at the stage of 8-32 cells) are transferred to surrogate moms after mating or artificial insemination with the sperm of an elite bull.
Fisheries

Source: Fisheries
- Fishery refers to capturing, processing, and selling fish, shellfish, and other aquatic creatures.
- Catla, rohu, and common carp are the most prevalent freshwater fish.
- Hilsa, sardines, mackerel, and pomfrets are all common marine fish.
- Aquaculture and pisciculture are two approaches that have been used to boost productivity.
- The growth in fish and other aquatic creatures is linked to the Blue Revolution.
- Aquaculture is the practice of commercially breeding and producing aquatic flora (fish, mollusks, crustaceans) and fauna (aquatic plants and algae).
- Intensive aquaculture occurs in ponds and tanks, whereas extensive aquaculture takes place in seas, rivers, or lakes.
- Pisciculture is the growing of fish to produce edible fish and fish products.
- Different fishes are cultivated together in polyculture, and different species are cultivated separately in monoculture.
Bee-keeping (Apiculture)

- Beekeeping, also known as apiculture, is the practice of keeping honeybee colonies in order to produce honey.
- Honey is a nutrient-dense food that is also used in traditional medicine, and Beeswax is also produced.
- Apis indica is the most prevalent honey bee species. The following considerations are critical for beekeeping success:
- Understanding the nature and habits of bees is essential.
- Choosing an appropriate place for the beehives
- Swarm catching and hiving
- Managing beehives at different times of the year
- Honey and beeswax handling and gathering
- Maintaining beehives in agriculture fields boosts pollination efficiency and productivity during the flowering season.
